How VeloCut X Diamond Tooling Is Manufactured
VeloCut X diamond tooling is engineered to meet the specific demands of grinding, polishing, and coating removal. While all diamond tools use industrial-grade diamonds, the manufacturing process varies depending on the bond type—metal-bond, resin-bond, or PCD—so that each tool performs optimally for its intended application.
Metal-Bond Diamond Tooling
- Mixing the bond – Metal powders (such as cobalt, bronze, or iron alloys) are blended with industrial diamond grit. The ratio of metal to diamond determines the tool’s aggressiveness and durability.
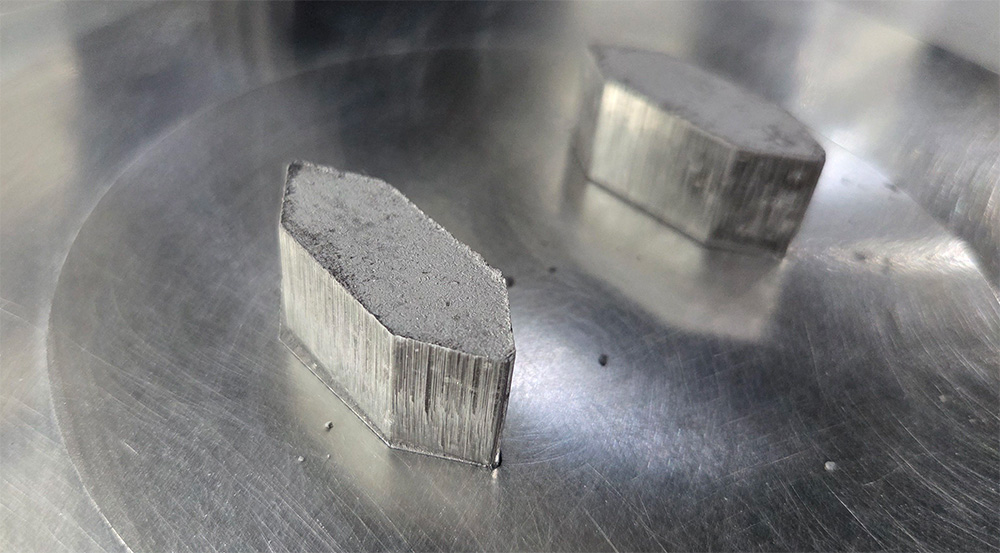
- Pressing the segments – The powder and diamond mixture is pressed into molds under high pressure to form the desired segment shape.
- Sintering – Segments are heated in a sintering furnace at controlled temperatures. This process fuses the metal particles together and locks the diamonds in place.
- Assembly – Finished segments are brazed or welded to a metal tool body (such as a grinding plate or cup wheel).
- Finishing – The tool is balanced and inspected for quality before packaging.



Resin-Bond Diamond Tooling
- Bond formulation – Resin powders (often phenolic resins) are mixed with diamond grit and, in some cases, metal fillers to enhance performance.
- Molding – The mixture is poured into molds shaped for polishing pads or segments.
- Hot pressing – Heat and pressure cure the resin, binding the diamonds into a solid form.
- Attachment – Pads are backed with Velcro, foam, or other mounting materials for use on polishing machines.
- Quality control – Each tool is tested for grit accuracy, bond hardness, and surface finish capability.
PCD Diamond Tooling
- PCD segment production – PCD (polycrystalline diamond) is made separately by sintering diamond particles together under extreme pressure and temperature, forming a single, ultra-hard diamond structure.
- Shaping – PCD segments are cut to the correct size and geometry, often with a laser or EDM (electrical discharge machining).
- Mounting – PCD segments are brazed onto a metal tool body designed for high-torque grinding machines.
- Final inspection – Tools are checked for bond integrity, segment positioning, and removal efficiency.
The Result
Each bond type is manufactured with its intended purpose in mind—metal-bond for aggressive grinding and surface leveling, resin-bond for fine honing and polishing, and PCD for rapid coating removal. Together, they form a complete toolkit for efficient, high-quality surface preparation.
